Reviewed by: Jos van den Nouwland – Product Manager for CG Drives & Automation
The key mechanism
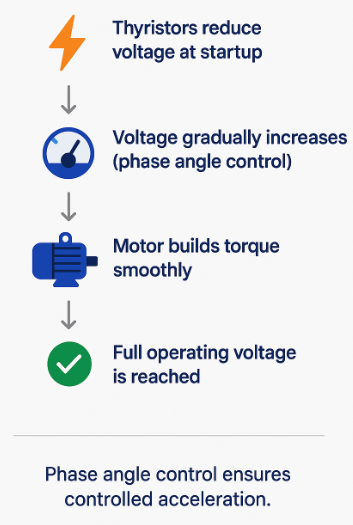
A softstarter reduces starting current by lowering supply voltage during startup. It does this through phase angle control using thyristors, gradually increasing voltage until the motor reaches full operating level.
Lower voltage results in lower current, which builds torque in a controlled way. This prevents sudden inrush currents and mechanical shocks while keeping the system stable.
Why starting current matters
When a motor starts directly on the grid, it can draw six to eight times its rated current. This surge can cause:
- Voltage dips that disturb sensitive equipment.
- Higher demand charges from utilities.
- Mechanical wear on shafts, couplings, and bearings.
By reducing the initial current, a soft starter provides smoother operation, lower stress, and improved reliability.
What happens in a Direct-On-Line start?
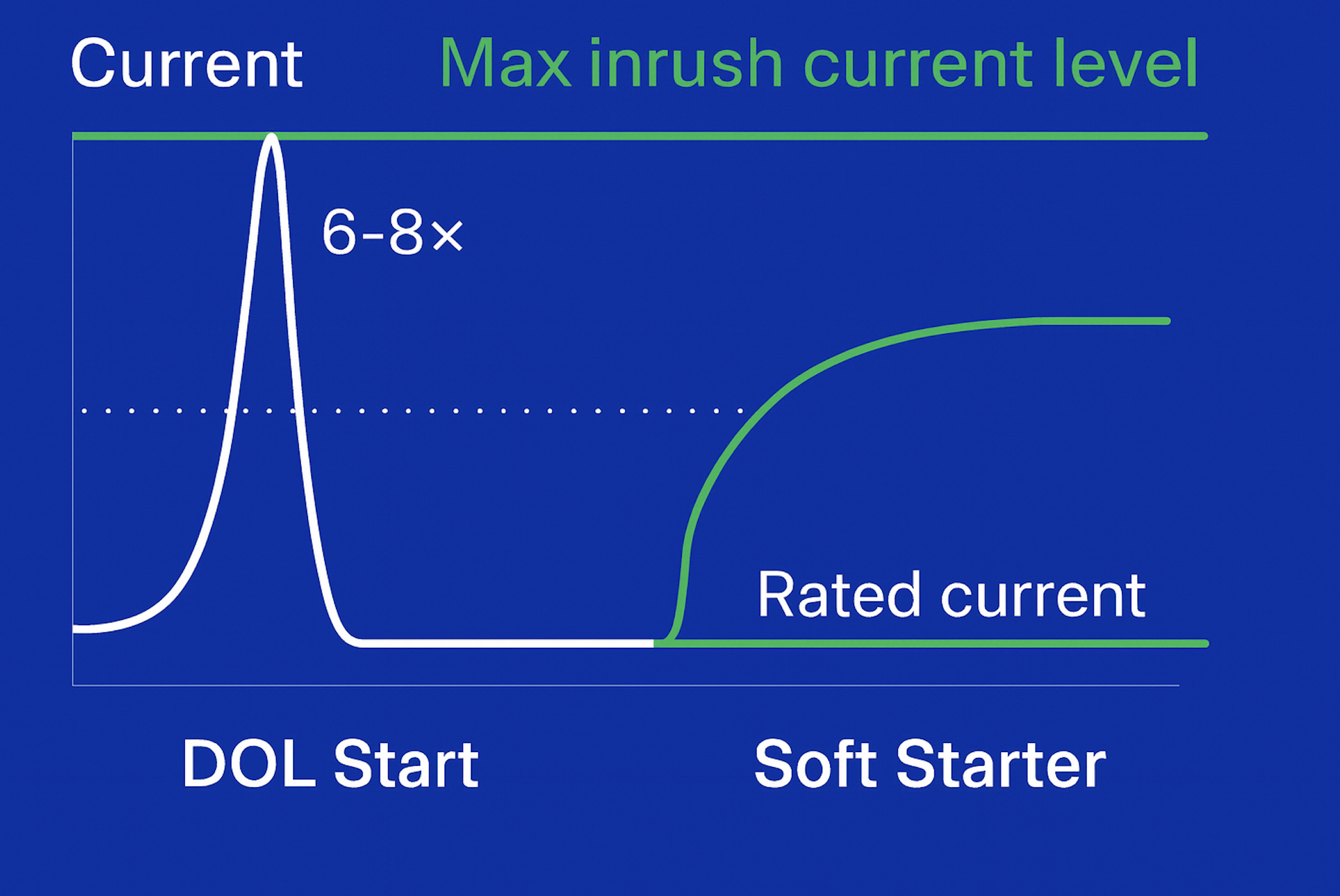
In a direct-on-line (DOL) start, the motor is connected to full line voltage immediately. Since no back electromotive force (EMF) exists at startup, the current surges dramatically.
Consequences include:
- System-wide voltage drops.
- Mechanical stress and reduced equipment lifespan.
- Water hammer in pump systems, damaging pipes and valves.
- Process disruptions in industrial operations.
A soft starter eliminates these issues by ramping voltage gradually, allowing the motor to build speed and torque smoothly.
The problem with DOL (Direct-On-Line) starting
When an induction motor starts directly, it usually draws 5 to 8 times its rated current. However, the starting torque is only 0.5 to 1.5 times the rated torque.
This causes several issues:
The electrical supply must be oversized to handle the high inrush current.
The sudden torque can cause mechanical stress and wear, reducing equipment life.
There’s no real performance gain from such high torque for most industrial applications
Soft starters vs. Capacitors
Capacitors and soft starters serve very different roles.
- Soft starters actively control voltage during motor acceleration, reducing inrush current and mechanical stress.
- Capacitors are static devices used for power factor correction or phase balancing.
A capacitor cannot replace a soft starter, as it does not manage motor torque or limit startup current.
Benefits of reducing starting current
Controlling startup current with a soft starter provides several advantages:
- Reduced mechanical wear on motors and driven equipment.
- Lower electrical stress on cables, breakers, and transformers.
- Elimination of water hammer in pump installations.
- Potential use of smaller power cables.
- Lower utility demand peaks and associated charges.
- Extended lifespan for motors and connected systems.
Subscribe to our industrial control newsletter
Find the root cause—not just the symptom
Don’t just clear the fault and restart. Understand why the issue occurred:
- Overcurrent might result from a blocked load or too heavy load
- Overvoltage could be from regenerative braking without proper resistors
- Phase loss might indicate a failed fuse or loose connection
Do soft starters extend a motor’s life?
Simple answer is Yes! For large industrial motors, reducing mechanical and thermal stress during startup can significantly extends service life. Bearings, shafts, and windings all last longer.
For smaller motors, the lifetime benefit is less dramatic, but system stability improves, and electrical stress is reduced.
When a soft starter is the right choice
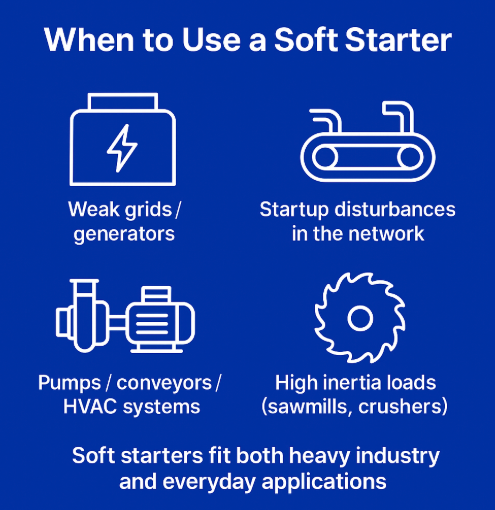
Soft starters are effective not only for heavy-duty motors but also in everyday applications where smoother starts are valuable. They are particularly useful when:
- Power supply is limited, such as on generators or weak grids.
- Startup creates disturbances for other connected equipment.
- A controlled torque profile is required for process stability.
- Smooth acceleration and braking reduce wear in pumps, conveyors, and HVAC systems.
- High-inertia loads, such as sawmills or crushers, need controlled starting and stopping.
Correct sizing and installation
A soft starter must be properly sized and configured to match the motor and load. If the initial voltage is set too low or the ramp time too long, torque may be insufficient for startup. If undersized, the device may overheat or reduce efficiency.
Correct selection ensures safe, reliable, and efficient operation.
Need help choosing the right soft starter? [Contact one of Emotron’s experts today]
Clearing up misunderstandings
- Soft starters are not energy-saving devices during steady-state operation; they only reduce current during startup.
- They are not limited to large motors — small and medium motors benefit as well.
- They are not energy storage devices and cannot replace capacitors.
- They are not a universal solution; correct application and configuration are key.
Commonly asked questions
Does a soft starter save energy?
Not during normal operation. It reduces peak demand during startup, which can lower utility charges and mechanical wear.
Can I use a soft starter on any motor?
Soft starters work well with most induction motors. However, they should be configured and set up for the specific load and use.
Why not just use a DOL starter?
Direct-on-line starters are cheaper, but they expose the system to high current surges and mechanical stress, which increases costs over time.
In conclusion
Soft starters are a smart and cost-effective way to limit the starting current of motors. They help reduce mechanical stress and protect connected systems. They ensure smoother operation, improved reliability, and longer equipment life.
Learn how Emotron’s soft starters can optimize your motor performance and protect your investment. [Request a free consultation (+46 42 16 99 00) or [Deep dive in our soft starter PDF].
